Urban System Projects
at the Visualization Center TESSIN VISLab
Here is a selection of our visualisation studies for urban systems:
Energy system infrastructure and storage
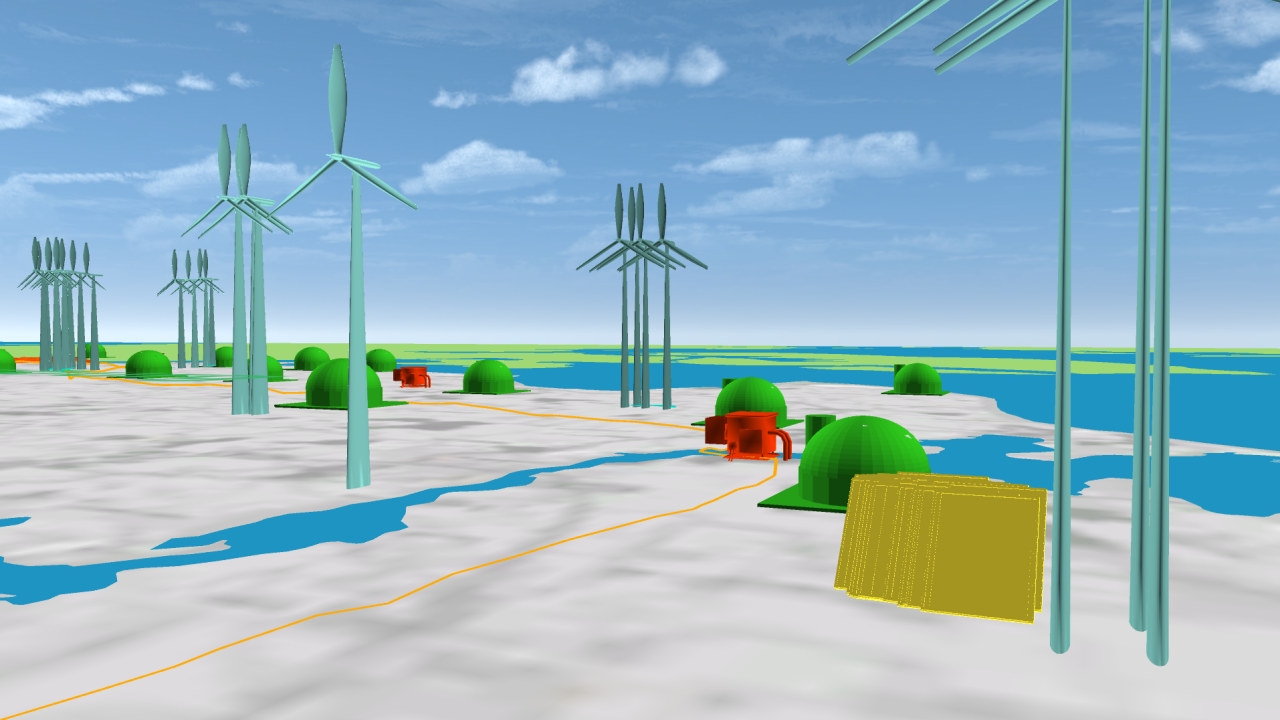
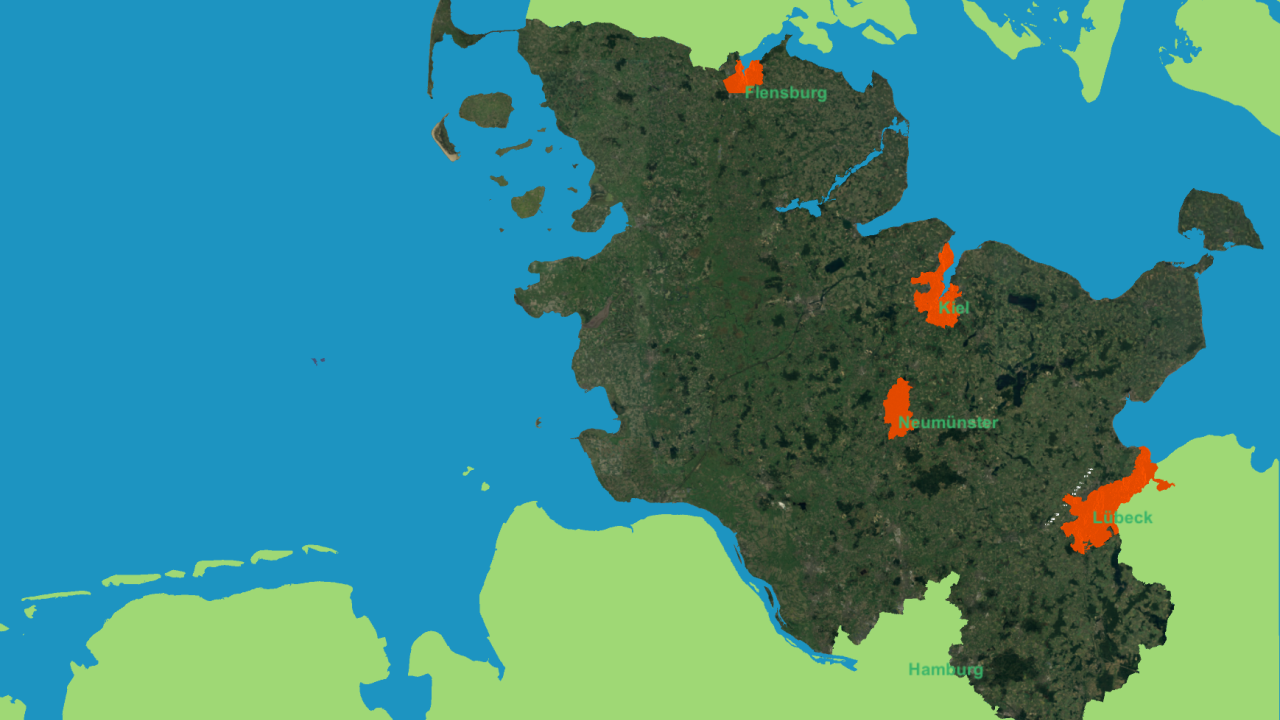
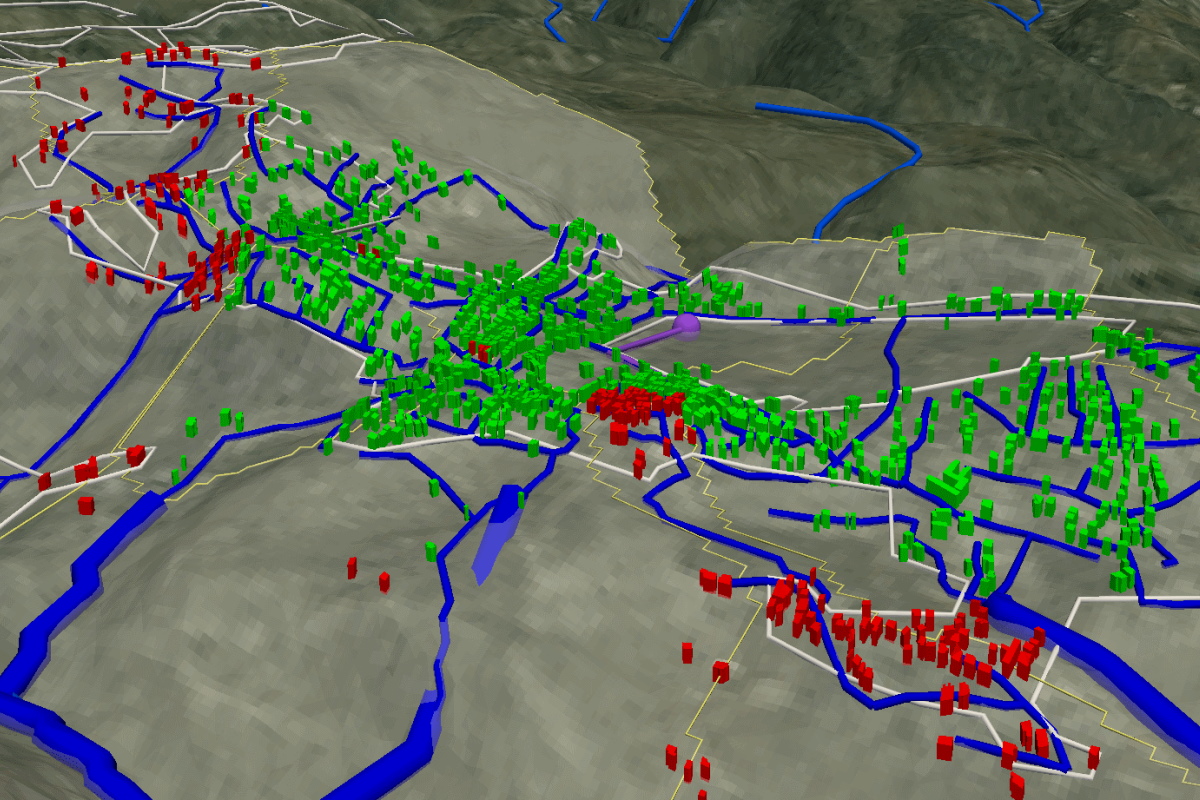
An environmental information system for the state of Schleswig Holstein, Germany, has been set up, integrating GIS data on renewable energy sources and infrastructure, topographical models, and subsurface information for an overview of the current state of renewable energy production. Simulation results for a compressed air energy storage in the stratigraphic formations and an aquifer thermal energy storage for a district of the city of Kiel demonstrate options for large scale energy storage in the subsurface. Adding the spatially discritised heat demand completes the overview of the current energy system infrastructure.
Video
Schleswig-Holstein Energy Systems Demo
Project Links
ANGUS IIPublications
- Rink, K, ÖO Şen, M Schwanebeck, et al. (2022): An Environmental Information System for the Exploration of Energy Systems. Geotherm Energ 10, art. 4. DOI:10.1186/s40517-022-00215-5
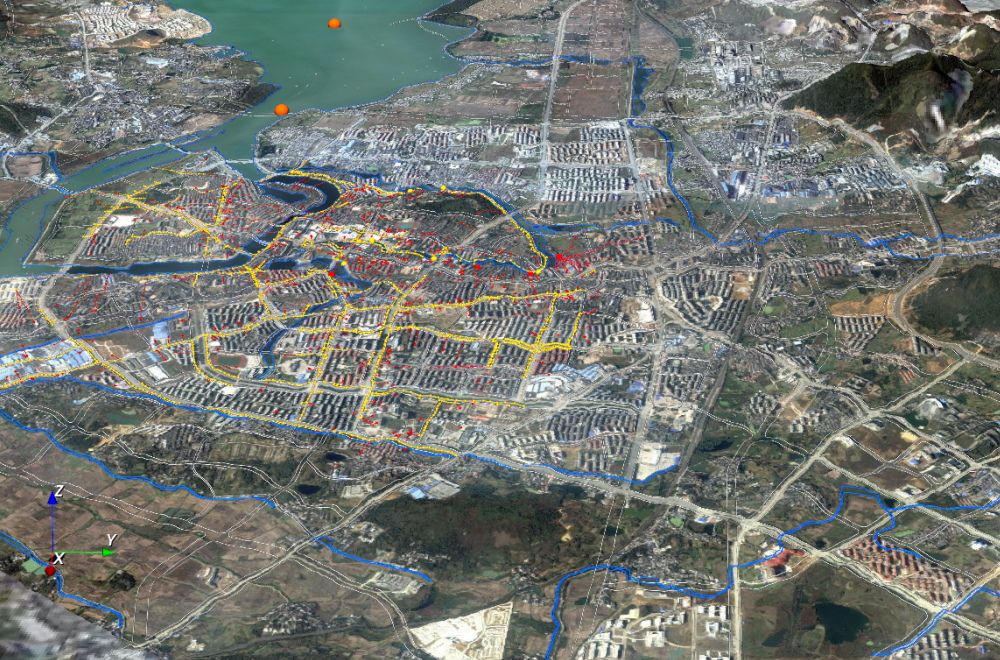
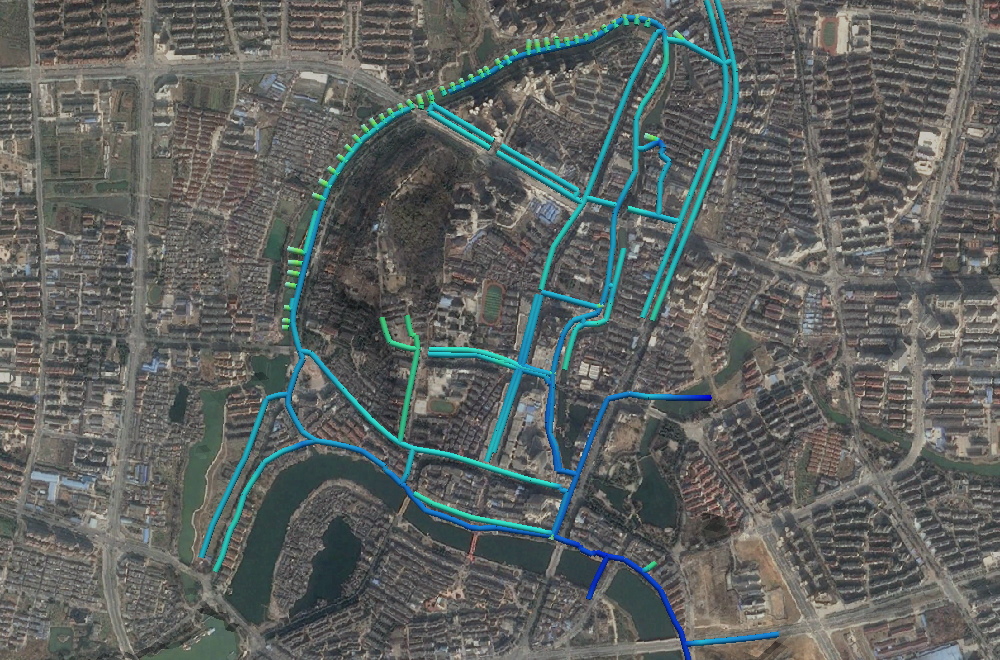
Urban Infrastucture and Water Systems
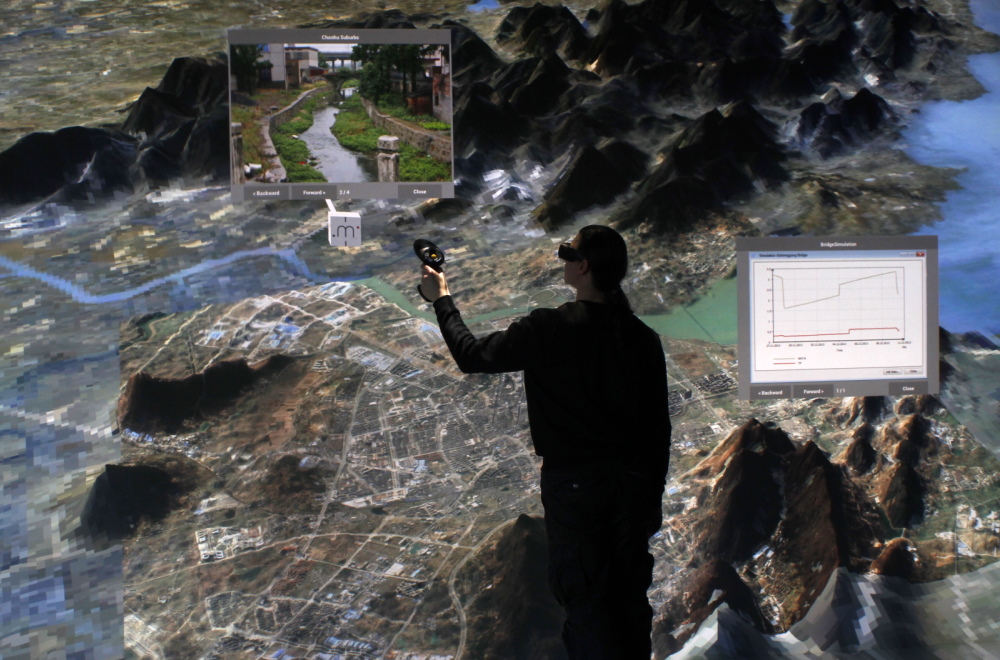
Data and model integration for urban water systems of Chaohu Lake, China and the city of Chaohu itself. Included are a wide range of environmental data as land use, streams, channels, the lake, as well as online monitoring systems. Integrated into the resulting 3D scene are results from numerical simulations of the Lake (via GETM), the groundwater within the lake catchment (via OpenGeoSys) and the sewage system and storm water channels in the city of Chaohu (via SWMM).
Video
Urban Catchments Demo
Project Links
Urban CatchmentsPublications
- A. Sachse, Z. Liao, W. Hu, et al. (2019): Chinese Water Systems – Volume 2: Managing Water Resources for Urban Catchments: Chaohu. Springer, Cham. ISBN: ISBN: 978-3-319-97567-2
- Rink, K., C. Chen, L. Bilke, et al. (2018). Virtual geographic environments for water pollution control. Int J Dig Earth 11 (4), pp. 397–407. DOI:10.1080/17538947.2016.1265016
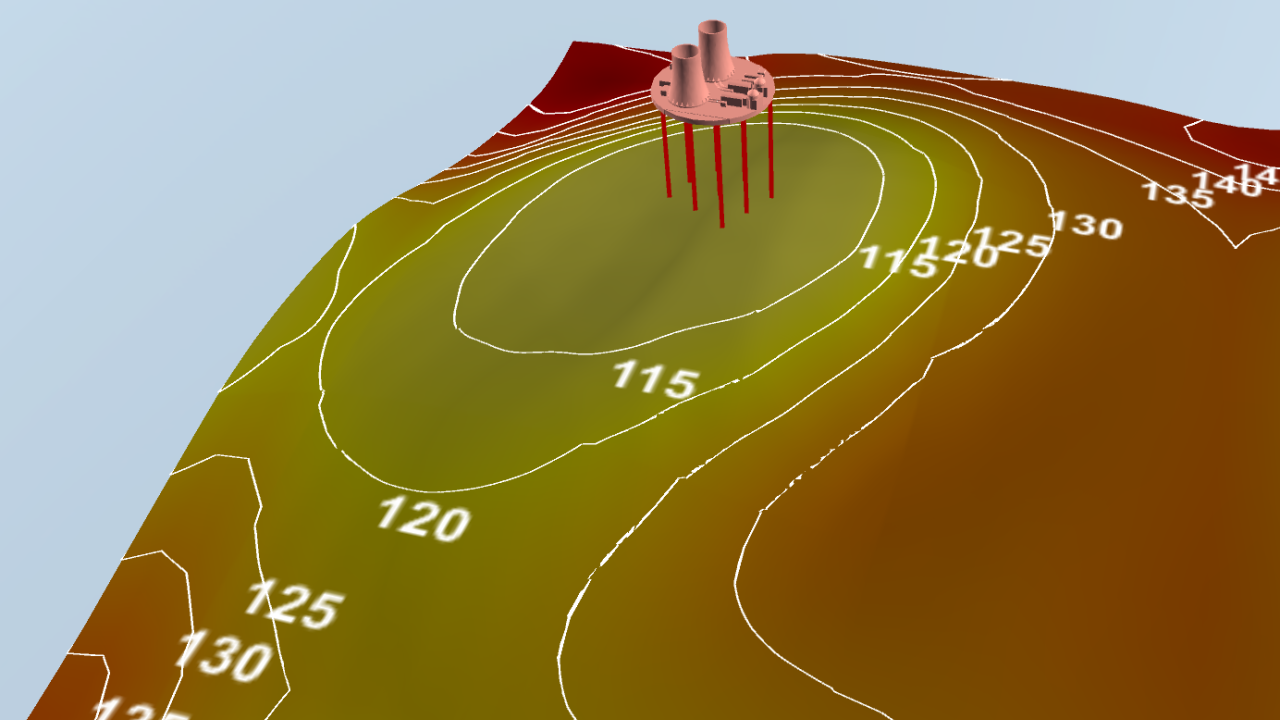
Shallow Geothermal Energy Systems
Visualisation for the planning of ground source heat pump systems for heating and cooling supply of a new residential district in the North of Leipzig, Germany. Included are representations of subsurface structures acquired by geophysical exploration in combination with borehole heat exchangers and the simulated groundwater level.
Video
Shallow Geothermal Systems, Geothermal Systems Chaohu
Project Links
SAGS, ANGUS+, EASyQuartPublications
- Vienken, T., S. Schelenz, K. Rink, and P. Dietrich (2015): Sustainable Intensive Thermal Use of the Shallow Subsurface – A Critical View on the Status Quo. Groundwater 53 (3), pp. 356–361. DOI:10.1111/gwat.12206
- S Chen, F Witte, O Kolditz, H Shao (2020): Shifted thermal extraction rates in large Borehole Heat Exchanger array – A numerical experiment. Applied Thermal Engineering 167, art. 114750. DOI:10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2019.114750
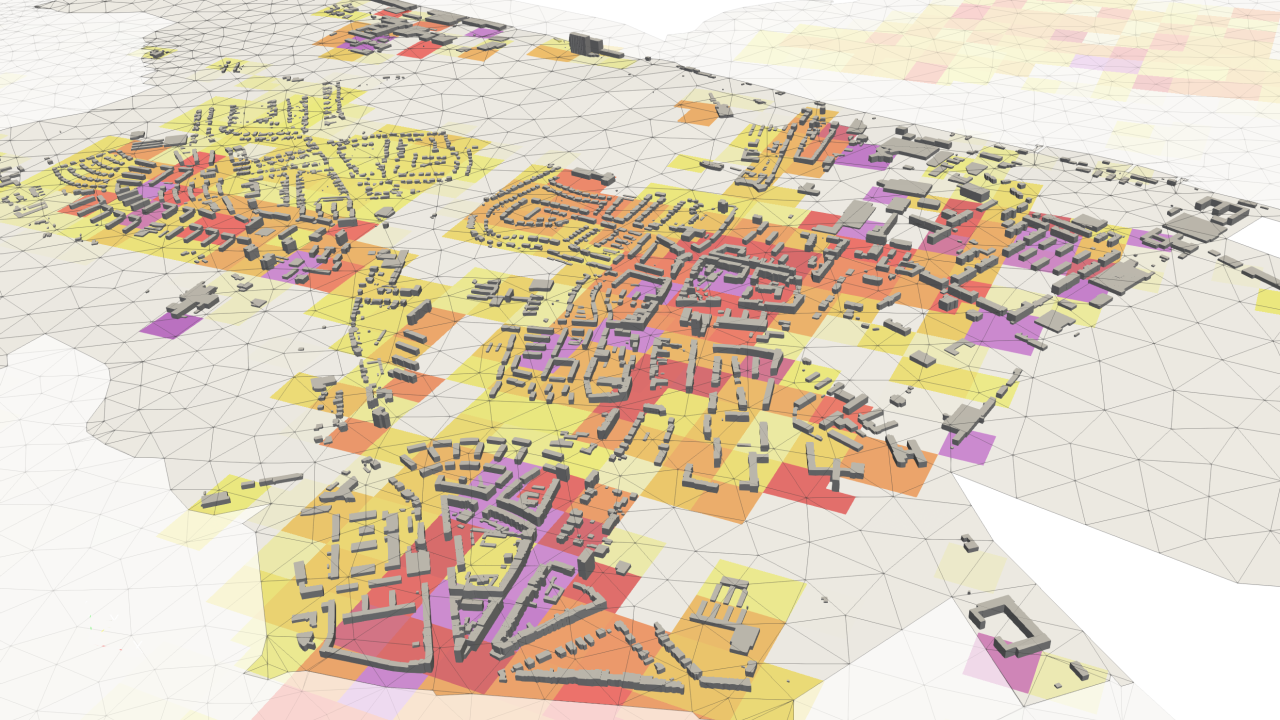
Urban Climate
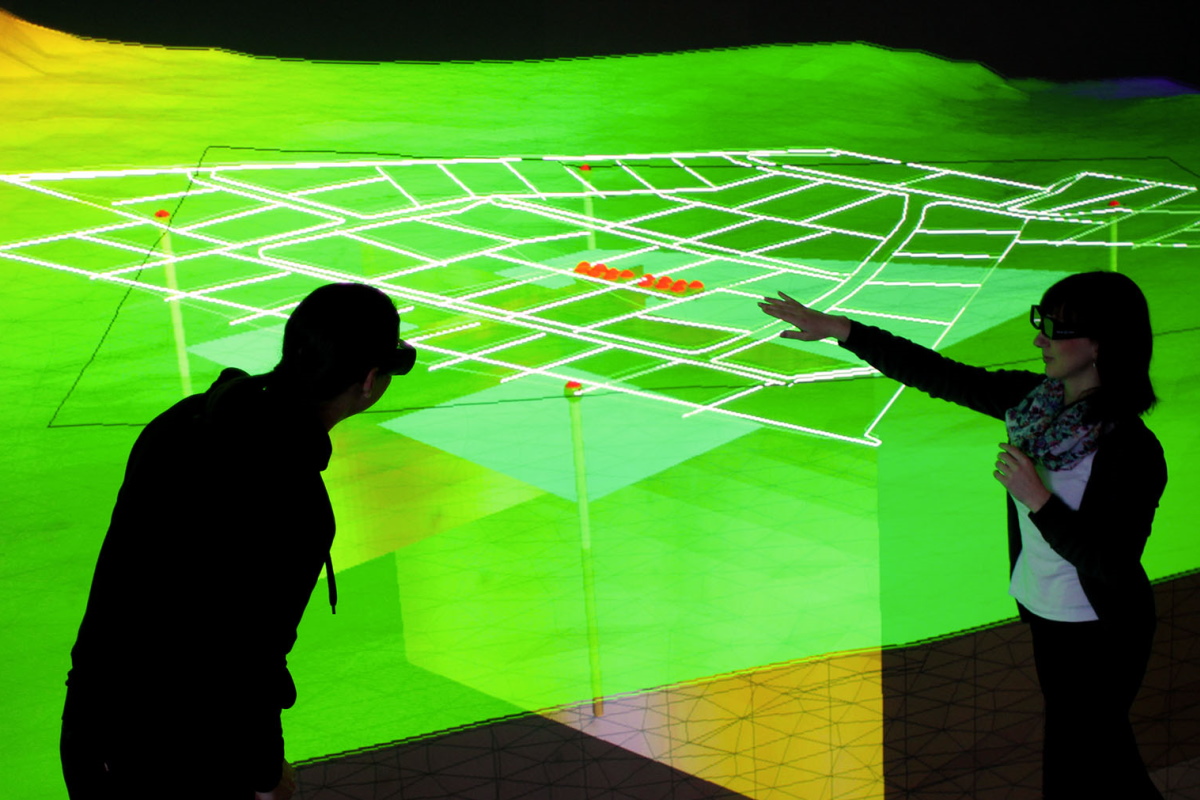
The influence of the absence or presence of buildings on urban microclimate is simulated and depicted in the actual building plan for a quarter within the city of Leipzig, Germany, including simulated wind directions and their influence on temperatures at different elevations.
Publications
- F Koch, L Bilke, C Helbig, U Schlink (2018): Compact or cool? The impact of brownfield redevelopment on inner-city micro climate. Sustainable Cities and Society 38, 31-41. DOI:10.1016/j.scs.2017.11.021
Waste Water Treatment
Options for centralised vs decentralised waste water systems for small villages in Jordan, displayed in the 3D geographical context. Integrated are a wide range GIS data sets for various scenarios for fresh water and sewage systems for cost evaluation based on high-resolution digital elevation models.